212-204-0075
info@pyvot.tech
Electromembrane Extraction (EME)
Electromembrane extraction (EME) is a new sample extraction alternative to liquid-liquid extraction (LLE) and solid-phase extraction
(SPE). This article discusses the principle, how method development is performed, and provides some example data on recovery, repeatability, matrix effect, and matrix clean-up.
Electromembrane Extraction: A Modern Alternative to Liquid-liquid extraction (LLE) and solid-phase extraction (SPE)
Preparing complex biological samples like blood, plasma, or urine for analysis is a critical step in achieving accurate results. Traditional methods—liquid-liquid extraction (LLE) and solid-phase extraction (SPE)—are widely used but come with drawbacks.
- LLE requires large volumes of toxic solvents, is time-consuming, and can be difficult to automate.
- SPE improves throughput and automation but adds cost and still involves multiple manual steps.
A new technique, Electromembrane Extraction (EME), offers a promising solution
EME enables selective, efficient extraction of target analytes from complex matrices while reducing solvent use, simplifying workflows, and supporting automation.
Electromembrane Extraction (EME): A Powerful Alternative to LLE and SPE
Electromembrane Extraction (EME) is an advanced sample preparation technique designed to improve upon traditional methods like Liquid-Liquid Extraction (LLE) and Solid-Phase Extraction (SPE). EME offers faster, cleaner, and more selective extraction, especially for charged analytes in complex biological matrices.
EME works by applying a low electric current to drive charged compounds from the sample solution across a thin organic membrane (called a Supported Liquid Membrane or SLM), and into a clean aqueous acceptor solution. The SLM is housed within a polymeric membrane and filled with a water-immiscible solvent that ensures selective transfer of analytes based on their charge and hydrophobicity (log P value).
The setup uses two conductive containers (often specialized HPLC vials) separated by the membrane. The direction of the applied voltage depends on whether you’re extracting positively or negatively charged compounds.
Key Advantages of EME:
- Excellent selectivity for charged compounds
- Low solvent consumption and minimal sample prep
- 5–30 minute extraction time with agitation
- Direct compatibility with LC and LC-MS systems
EME is a smart solution for labs looking to streamline sample prep while improving sensitivity and selectivity.
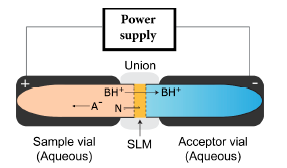
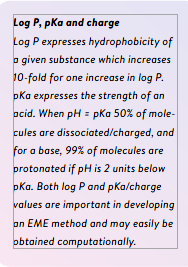
Figure 1. Illustration of the EME principle configured for the extraction of protonated bases (BH+). Due to the applied potential, deprotonated acids (A-) remain in the sample while Neutral species (N) form an equilibrium with the supported liquid membrane (SLM).
Advantages of EME:
Electromembrane Extraction (EME): A Smarter Alternative to LLE and SPE
Electromembrane Extraction (EME) is an advanced sample preparation technique that addresses many of the limitations of traditional Liquid-Liquid Extraction (LLE) and Solid-Phase Extraction (SPE). Offering a cleaner, faster, and greener approach, EME is ideal for complex biological samples and LC-MS workflows.
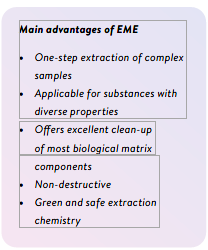
- Efficient One-Step Sample Preparation
- EME simplifies the extraction process by converting complex matrices — like whole blood or tissue homogenates — into a clean aqueous extract in a single step, ready for direct injection into LC or LC-MS systems. No additional cleanup required.
- Microextraction with Minimal Solvent Use
- EME uses just 0.01–0.03 mL of organic solvent per sample — a 100–1000-fold reduction compared to LLE or SPE. This ultra-low solvent volume classifies EME as a microextraction technique, supporting cost savings and environmentally responsible lab practices.
- Dual Selectivity for Cleaner Results
- By combining electrokinetic migration (charge-based) and membrane partitioning (hydrophobicity-based), EME achieves high selectivity. It effectively removes proteins, phospholipids, and other matrix interferences, preventing LC column clogging and reducing ion suppression in MS detection.
- Non-Destructive and Reversible
- Unlike many extraction methods, EME is non-destructive. The original sample remains available for reuse or further analysis, making it particularly valuable in limited-sample applications or for confirmation testing.
- Targeted Removal of Interferences
- EME can be optimized to selectively extract desired analytes or remove specific unwanted compounds, providing added flexibility for method development or sample-specific challenges.
- Environmentally Friendly & Lab-Safe
- EME relies on non-volatile, non-toxic solvents in very small amounts, making it a greener alternative to conventional extraction methods and reducing hazardous waste in the lab.
- EME relies on non-volatile, non-toxic solvents in very small amounts, making it a greener alternative to conventional extraction methods and reducing hazardous waste in the lab.
In short, EME offers a cleaner, simpler, and more sustainable approach to sample preparation, without compromising on performance. It’s an ideal solution for high-throughput labs, LC-MS users, and anyone looking to modernize their extraction workflow.
