31 Oct Novel end-capping method with silyl-reagent including ethylene chain
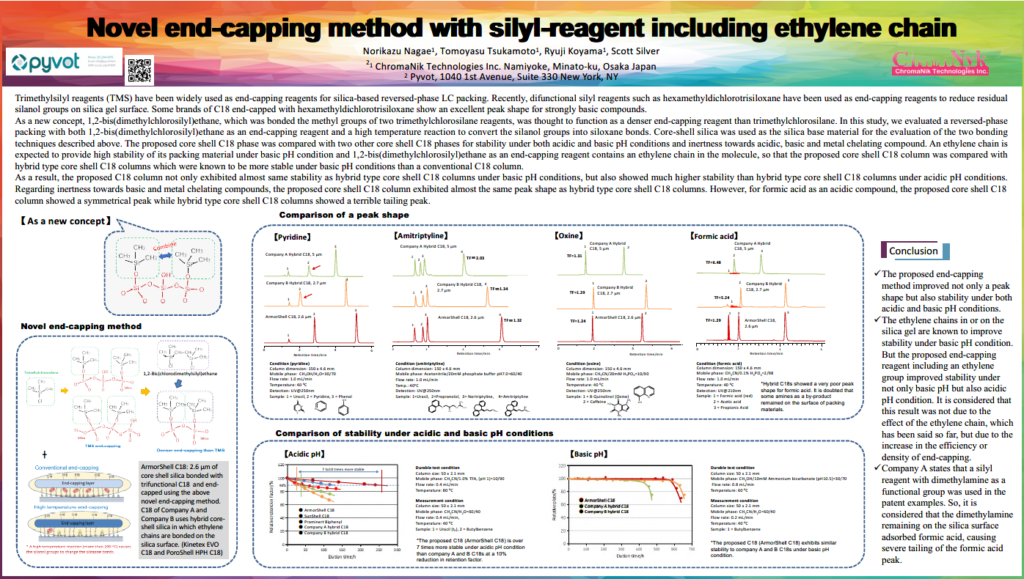
Trimethylsilyl reagents (TMS) have been widely used as end-capping reagents for silica-based reversed-phase LC packing. As a new concept, 1,2-bis(dimethylchlorosilyl)ethane, which was bonded to the methyl groups of two trimethylchlorosilane reagents, was thought to function as a denser end-capping reagent than trimethylchlorosilane. In this study, we evaluated a reversed-phase packing with both 1,2-bis(dimethylchlorosilyl)ethane as an end-capping reagent and a high-temperature reaction to convert the silanol groups into siloxane bonds. A core-shell silica was used as the silica base material. An ethylene chain is expected to provide high stability of its packing material under basic pH conditions and 1,2-bis(dimethylchlorosilyl)ethane as an end-capping reagent contains an ethylene chain in the molecule so that the proposed core-shell C18 column was compared with hybrid type core-shell C18 columns. As a result, the proposed C18 column not only exhibited almost the same stability as hybrid-type core-shell C18 columns under basic pH conditions but also showed much higher stability than hybrid-type core-shell C18 columns under acidic pH conditions. Regarding inertness towards basic and metal chelating compounds, the proposed core-shell C18 column exhibited almost the same peak shape as hybrid-type core-shell C18 columns. However, for formic acid as an acidic compound, the proposed core-shell C18 column showed a symmetrical peak while hybrid-type core-shell C18 columns showed a terrible tailing peak.