212-204-0075
info@pyvot.tech
HPLC 2025
Evaluation of Durability of Hybrid Silica with Ethylene Chains
Chromanik Technologies recently introduced Sunbridge C18, a new hybrid silica material in which the silica gel is cross-linked with ethylene chains. This structure differs from other hybrid technologies that consist of Ethylene chains bonded to the silica gel surface. A detailed comparison of hybrid silica types is presented in this poster.
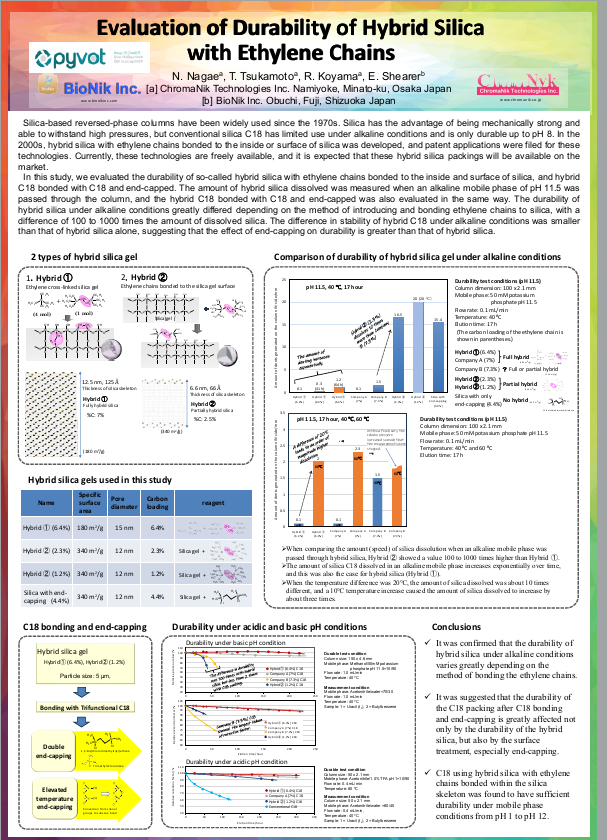
We compare Chromanik’s Sunbridge hybrid silica (referred to as Hybrid 1), featuring an ethylene cross-linked silica gel with a 6.4% carbon loading, including Chromanik’s proprietary bonding (end capping) technology.
Included in the poster:
- Evaluation of silica durability under alkaline conditions, beginning at pH 11.5, 40 °C for 17 hours, and extending to higher temperatures and longer exposure times.
- Comparative analysis of silica dissolution across different hybrid technologies.
- Durability performance under both acidic and basic pH conditions.
Sunbridge hybrid silica demonstrates excellent chemical stability and resistance to dissolution, showing superior durability across a range of challenging conditions.
Company A in the presentation is the XBridge BEH C18.
Evaluation of Bidentate End-Capping Silylation Reagents for HPLC
This poster explores how different silica-based materials and end-capping chemistries impact the performance and durability of C18 HPLC columns. Six packing materials were created by combining three types of silica and combining it with two end capping technologies. All of these were compared to the technology of Company W Hybrid.
These include:
1.Hybrid 1 Ethylene cross-linked silica gel (Chromanik Sunbridge C18 Hybrid)
2. Hybrid 2 Ethylene chains bonded to the silica gel surface (Chromanik SunArmor C18 Hybrid)
A Type End Capping 1,5-Dichlorohexamethytrisiloxane
B Type End Capping 1,2-Bis(chlorodimethylsilyl)ethane
Silica Gel C18 (Chromanik Sunniest C18)
Company W Waters XBridge BEH
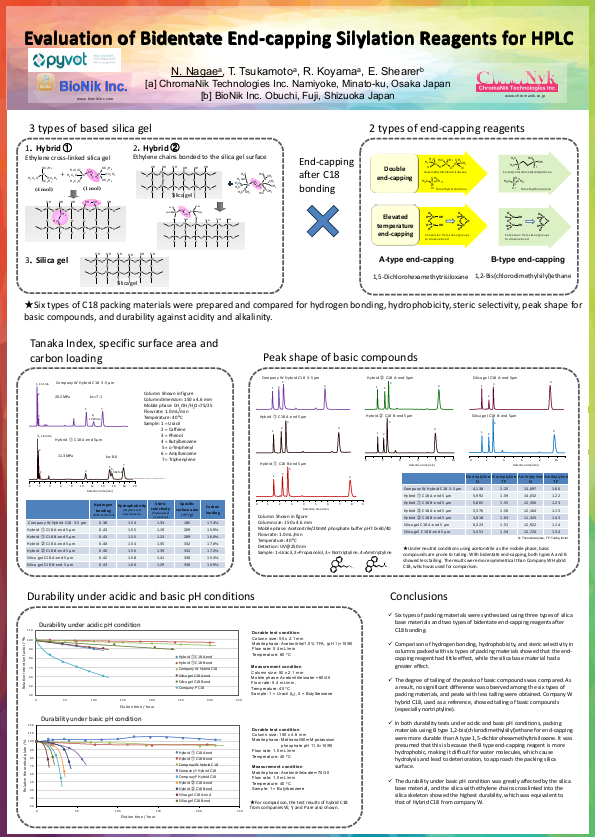
Key findings show that the silica base material had a greater effect on hydrogen bonding, hydrophobicity, and steric selectivity than the end-capping reagent. All six columns provided sharp peaks for basic compounds with minimal tailing, performing better than a reference hybrid (Waters XBridge BEH), which showed significant tailing with nortriptyline.
In durability studies, columns capped with a more hydrophobic end-capping reagent (1,2-bis(chlorodimethylsilyl)ethane) were more stable under acidic and basic conditions. The silica with ethylene crosslinking in its structure offered the highest resistance to degradation at high pH, matching the durability of the reference hybrid C18 column (Waters XBridge BEH).
Evaluation of Hybrid Silica C18 End-capped with Bidentate Silylating Reagent for HPLC
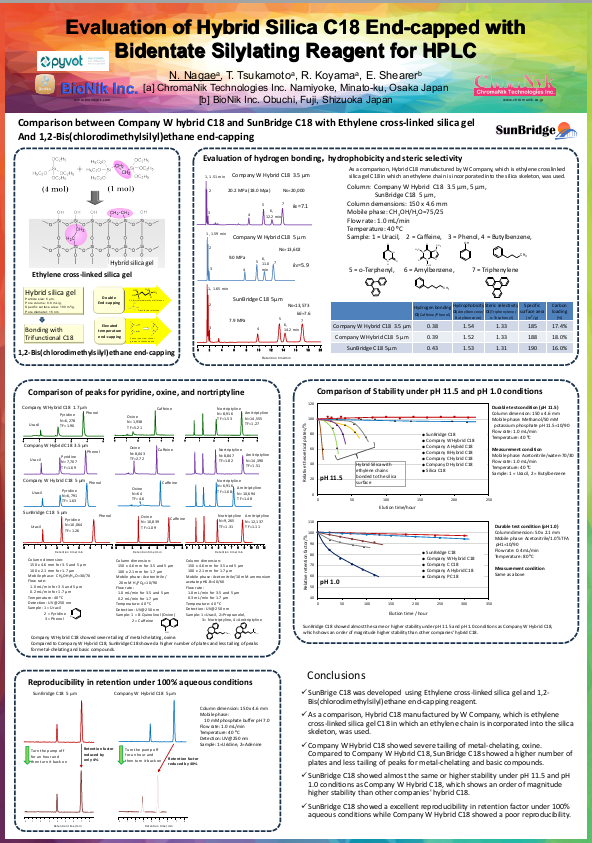
This poster highlights a comparative study between SunBridge C18, a novel column developed using ethylene cross-linked silica gel with 1,2-Bis(chlorodimethylsilyl)ethane end-capping, and a Waters XBridge BEH (Company W), which also uses ethylene cross-linked silica.
Key Findings:
- Reduced Peak Tailing: SunBridge C18 showed significantly less tailing for challenging compounds like oxine and other metal-chelating or basic analytes, where Waters XBridge BEH exhibited severe tailing.
- Higher Efficiency: It delivered a greater number of theoretical plates, indicating sharper and more efficient separations.
- Excellent pH Stability: Comparable or better stability was observed for SunBridge C18 under extreme pH conditions (pH 1.0 and 11.5), matching the high durability expected from hybrid silica columns.
- Excellent Reproducibility: Under 100% aqueous mobile phase conditions, SunBridge C18 maintained consistent retention factors, whereas Company W’s hybrid column showed poor reproducibility.
These results suggest that SunBridge C18 offers a compelling alternative for analysts seeking high performance and robustness in reversed-phase HPLC, especially when working with polar or metal-interacting compounds
Analysis of PFAS in Tap Water Using a Pentafluorophenyl Column
New PFP Column Offers Enhanced PFAS Detection for Drinking Water Analysis
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), often called “Forever Chemicals,” are persistent environmental pollutants linked to health risks and commonly found in water, food, and consumer products. Accurate and sensitive PFAS analysis has become increasingly critical.
This poster introduces a new SunBridge PFP-R column, built on an ethylene cross-linked hybrid silica gel and coated with a pentafluorophenyl (PFP) stationary phase, designed specifically for comprehensive PFAS analysis. The column successfully separated 19 PFAS compounds, including short-chain and long-chain variants, with greater sensitivity for PFBA and better resolution of PFHxS isomers compared to conventional C18 columns.

The hybrid silica design also supports longer column life, making SunBridge PFP-R a powerful tool for high-sensitivity, high-resolution PFAS monitoring in tap water and environmental samples.
