212-204-0075
info@pyvot.tech
Synthetic Adsorbents
DIAION™ & SEPABEADS™ Synthetic Adsorbents
GENERAL FEATURES
Synthetic adsorbents are a series of products based on ion exchange resin manufacturing technology and are designed for use as solid extractants. Synthetic adsorbents have large surface areas and fine pore structures inside the particle-like activated carbon. For this porous characteristic, they can effectively adsorb organic compounds from aqueous solutions. Extraction processes with synthetic adsorbents enable reducing the solvent amount and safer operations compared with conventional solvent extraction techniques.
PROPERTIES
A synthetic adsorbent is a spherical particle, and inside it, there exist effective fine pore structures suitable for the diffusion of solutes.

Smaller solutes can penetrate into the particle by diffusing through the pores when a solution is allowed to contact with adsorbent particles.
On the contrary, molecules that are larger than pore size cannot penetrate into the inside of particles. Consequently, such molecules are not adsorbed on synthetic adsorbents (this phenomenon is the so-called molecular sieving effect).
APPLICATION FIELDS
Synthetic adsorbents are used for the separation of valuable compounds from plant extracts and fermentation products for pharmaceutical intermediates and food additives.
STABILITY
Synthetic adsorbents are stable in acidic, alkaline solutions and in organic solvents, and they can be easily regenerated under mild conditions for repeated uses.
TECHNICAL MANUAL
TYPES OF SYNTHETIC ADSORBENTS AND SELECTION GUIDE CHEMICAL STRUCTURE
There are three types of chemical structures for synthetic adsorbents; aromatic, modified aromatic and methacrylic series.
Mitsubishi’s_Synthetic_Adsorbents_List
The chemical structure dominates the degree of hydrophobicity of synthetic adsorbents. Hydrophobicity of adsorbent is important in selecting a suitable type of adsorbent according to the chemical nature of target compounds.
| Aromatic | Aromatic type adsorbents are the standard grade and are based on crosslinked polystyrene matrix. They are widely used in different industrial fields; extraction of antibiotic intermediates from the fermentation broth, separation of peptides, or food additives, debittering of citrus juice, etc. DIAION™ HP20 HP21 / SEPABEADS™ SP825L SP850 SP70 SP700 |
|---|---|
| Modified Aromatic | Modified aromatic type is based on a brominated aromatic matrix which gives enhanced hydrophobicity. This type adsrobent is suitable for adsorption of organic substances of very low concentration or of highly hydrophilic substances. SEPABEADS™ SP207 |
| Methacrylic | Methacrylic type is based on methacrylic ester copolymer, and has relatively hydrophilic nature. This type of adsorbent is suitable for adsorption of polyphenols and surfactants. DIAION™ HP2MGL |
PORE STRUCTURE
Mitsubishi Chemical supplies a wide variety of synthetic adsorbents with different pore structures. The most appropriate type of adsorbent can be selected according to the pore size of adsorbent and the molecular size of the target compound (or sometimes unfavorable compounds to be removed).
Another important parameter is surface area of resins. Adsorbent with large surface area shows high uptake capacity, especially for small molecules.
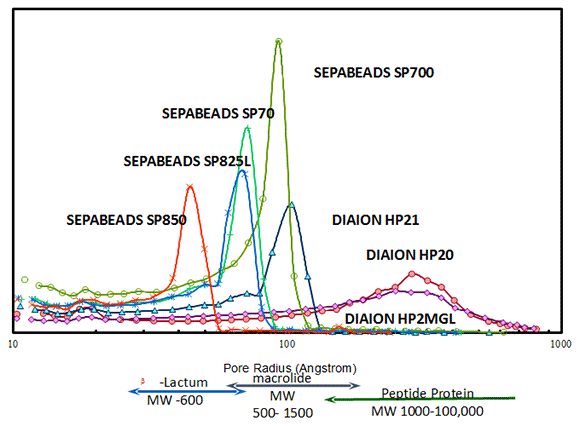
PORE SIZE DISTRIBUTION OF SYNTHETIC ADSORBENTS
Pore size is an important key parameter which determines the adsorptive characteristics of synthetic adsorbents.
Smaller pore adsorb only small molecules while larger molecules are excluded (molecular sieving effect). On the other hand, larger pores can adsorb large molecules such as proteins.
By selecting the appropriate size of pore according to the nature of the target substance, it is possible to establish more effective purification processes.
PARTICLE SIZE
Standard synthetic adsorbents have ca 0.5 mm mean particle diameter. This size is designed for most industrial scale processes.
SMALLER PARTICLE-SIZE ADSORBENTS
Smaller particle size adsorbents are used for fine separation/purification applications as reversed-phase chromatographic packing materials.
Synthetic Resins of Small Particle \-size for Chromatographical Separation
It is well known that smaller size resins are required to obtain higher purity and better recovery in chromatographic separation of pharmaceuticals. Mitsubishi Chemical offers several types of synthetic adsorbent grades in very useful particle size distributions for industrial scale chromatography.
Mitsubishi chemical also offers analytical HPLC packing media MCI GEL™ which has same chemical and physical structure as these grades. Industrial scaling up of separation process is easily attained by using our product line up.
Aromatic Type DIAION™ HP20SS, SEPABEADS™ SP20SS
HP20SS and SP20SS are directly polymerized, small particle size version of HP20. The wide pore polymer matrix provides excellent kinetics and capacity for small biomolecules at both preparative and process scale. They offer nice balance of pressure flow characteristics and true chromatographic fractionation and have also been successfully applied in simulated moving bed (SMB) applications for a variety of small biomolecules. They often compete with bonded silica supports for preparative and industrial applications.
Modified Aromatic Type SEPABEADS™ SP207SS
SP207SS is a small size version of modified aromatic type SEPABEADS™ SP207. It is applied to reversed phase chromatography. The brominated polymeric matrix provides unique selectivity, full pH operating range and long operating life versus conventional bonded silica packing materials used in preparative and industrial applications.
| Grade Name | DIAION™ HP20SS | SEPABEADS™ SP20SS | SEPABEADS™ SP207SS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | 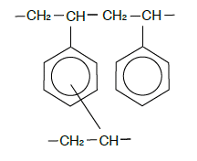 | 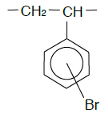 | |
| Shipping Density (g/ℓ-R; approx.) | 670 | 660 | 780 |
| Water Content (%) | 55-67 | 55-65 | 43-53 |
| Particle Size | on 150μm 63-150μm through 63μm 15% max. 70% min. 20% max. | on 75μm 63-75μm through 63μm 30% max. 55% min. 15% max. | on 150μm 63-150μm through 63μm 15% max. 70% min. 20% max. |
| Example of Porosity Pore Volume (㎖/g) Specific Surface Area (m2/g) Pore Radius (Å) | 1.2 560 290 | 1.0 590 110 | |
| Operating Temperature (℃) | 130 max. | 130 max. | |
Mitsubishi’s Synthetic adsorbent
| Chemical structure | Good point | Adsorption Ability | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Synthetic adsorbent of Styrene body HP20 / HP20SS / HP21 / SP70 / SP700 / SP825L / SP850 / CHP20 / CHP50 |  |
| strong |
| Synthetic adsorbent of bromated Styrene body SP207 |  |
| Very strong |
| Synthetic adsorbent of Methacryle ester body HP2MGL / CMG20 |  |
| Hydrophobic weak Hydrophilic strong |
Mitsubishi’s Synthetic adsorbents list
| Name | SP850 | SP825L | SP70 | SP700 | HP21 | HP20 | SP207 | HP2MGL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water content | 46-52% | 52-62% | 55-65% | 60-70% | 45-55% | 55-65% | 43-53% | 55-65% |
| Particle distribution (0.25mm) | ≥90% | ≥95% | – | – | ≥90% (0.25mm) | ≥90% (0.25mm) | ≥90% (≥300mm) | |
| Effective size (mm) | ≥0.25 | – | – | ≥0.25 | ≥0.25 | ≥0.30 | ||
| Uniformity coefficient | ≤1.6 | – | – | ≤1.6 | ≤1.6 | ≤1.6 | ||
| Mean diameter (mm) | – | – | 0.45 | 0.45 | – | – | – | – |
| Surface area (m2/g) (m2/mL) | 930 320 | 930 290 | 870 220 | 1200 280 | 640 190 | 590 160 | 600 250 | 570 150 |
| Pore volume (ml/g) | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 2.2 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.0 | 1.3 |
| Mode radius (Angstrom) | 45 | 70 | 70 | 90 | 110 | 290 | 110 | 240 |
| Cephalosporin C adsorption weight (g/L) | 85 | 76 | 60 | 76 | 48 | 38 | 119 | <10 |
Note: pre-distribution and CPC adsorption weight is a reference value
Scalability
[Key point]
- Easy to scale up
- We can offer separation media for all R&D stage.
| MCI™ GEL 3-10μm | MCI™ GEL 10-50μm | DIAION™ SEPABEADS™ 50-250μm | DIAION™ SEPABEADS™ >250μm | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organic compound | CHP20 / C04 CMG20 / C04 | CHP20 / P30 CHP50 / P30 CMG20 / P30 | SP20SS / HP20SS | HP21 HP20 HP2MGL |
| Sugar and Amino acid | CK Series CA Series | CK Series CA Series | UBK Series UMA Series | SK Series SA Series |
| Protein | XtalSpeed™ CQA Series CQK Series | MabSpeed™ ChromSpeed™ | FP-DA13 |
