Shop
BioChromato Slit Seal, 96 well plate seal
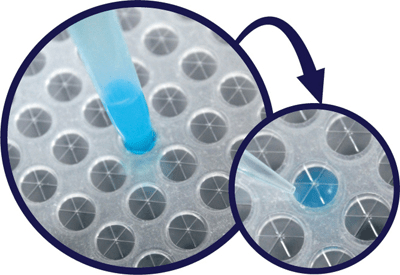
The Slit Seal is a resistant, instant self-closing 96-well plate seal.
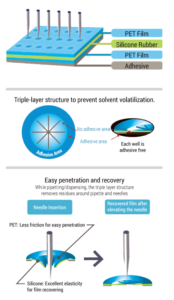
The adhesive-free. Pre-cut slits made of silicone and PET allows easy insertion and withdrawal of pipette tips and sampling needles without dragging. The Slit Seal’s main purpose is to prevent solvent evaporation and cross-contamination. Some suggested applications are automation, SPE, HPLC, LC/MS, and ADME.
Description
FEATURES:
- Self-closes instantly
- No cross-contamination between wells
- Allows next-day analysis
- No adhesive on well spots
- Pipette tips insert easily with less friction
- Reduce solvent evaporation
SPECIFICATIONS:
- Size: 80 mm x 122 mm (96-well format)
- Material: PET. Silicone
- Adhesive: Acrylic-based (no adhesive over well spots)
- Functional temperature range: -80°C to +37°C Automation
- No PCR inhibition
- If DNA-free certification is needed, please contact us
APPLICATIONS:
- Automated pipetting and liquid handling
- SPE
- HPLC and LC/MS
- ADME
- DNA Extraction
- Automated single-molecule imaging
- Cell culturing
- Biochemical assays
- Incubation
- Vortex
Publications
Ask, K. S., Lid, M., Øiestad, E. L., Pedersen-Bjergaard, S., & Gjelstad, A. (2019). Liquid-phase microextraction in 96-well plates calibration and accurate quantification of pharmaceuticals in human plasma samples. Journal of Chromatography A.
Toth, C. A., Kuklenyik, Z., & Barr, J. R. (2019). Nuts and Bolts of Protein Quantification by Online Trypsin Digestion Coupled LC-MS/MS Analysis. In Functional Proteomics (pp. 295-311). Humana Press, New York, NY.
Berg, T., Eliassen, E., Jørgenrud, B., Kabashi, S., Petukhov, A., & Bogstrand, S. T. (2018). Determination of phosphatidyl ethanol 16: 0/18: 1 in whole blood by 96‐well supported liquid extraction and UHPLC‐MS/MS. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis, e22631.
Yasui, M., Hiroshima, M., Kozuka, J., Sako, Y., & Ueda, M. (2018). Automated single-molecule imaging in living cells. Nature Communications, 9(1), 3061.